
Metagenomics tells a set of genomic technologies and bioinformatics tools to right access the genetic content of whole groups of organisms. The field of metagenomics has been stimulating with for considerable improvements in microbial ecology, diversity, and evolution.Metatranscriptomics is the study of the function and activity of the complete set of transcripts i.e RNA sequencing from environment samples.
Metagenomics is study of the genetic material that recovered straight from environmental sample. metagenomics is a molecular tool and techniques that used to detect DNA obtain from environmental sample to study the microorganisms present without the requirement of finding pure cultures. Metatranscriptomic sequencing provides straight access to culturable and non-culturable microbial transcriptome information by large-scale, high-throughput sequencing of transcripts from all microbial communities in specific environmental samples.
Introduction
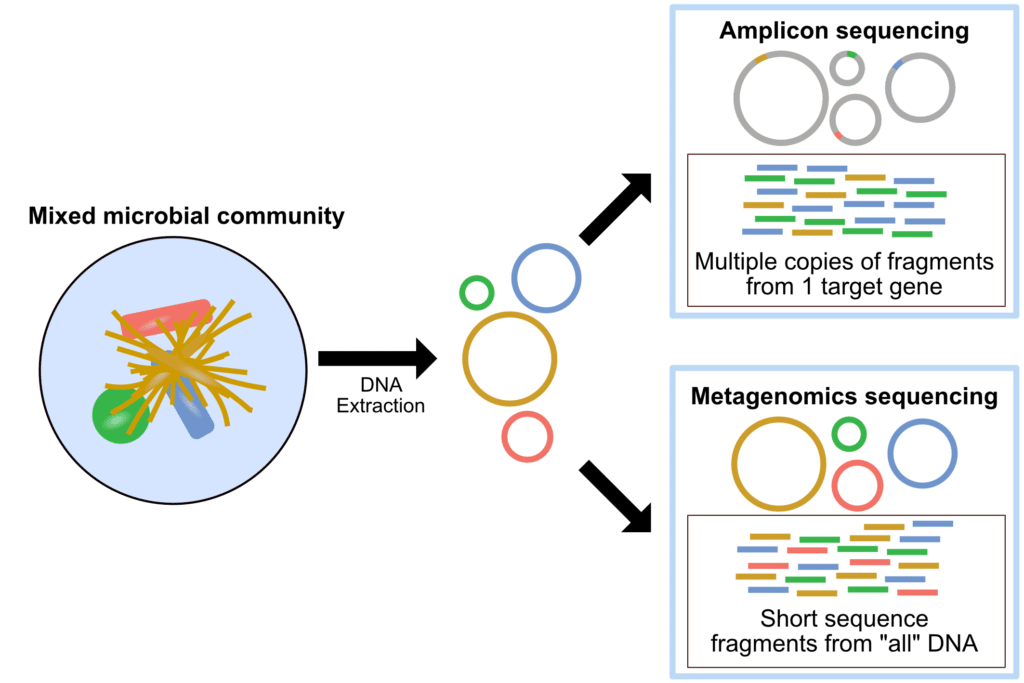
Metagenomics constructs a taxonomical process in the sample, metatranscriptomics helps us to obtain a metabolomics and functional profile and completes the picture by responsible which by products are being released into the environment. Metagenomics is the study of the genomes in a microbial groups and constitutes the first step to studying the microbiome using metatranscriptomics which involves sequencing the complete metatranscriptome of the microbial groups.
Metatranscriptomics inform the genes that are expressed by the group as a total. With the use of efficient annotations of expressed genes, it is possible to suppose the functional profile of a group under specific conditions, which are usually dependent on the status.
Metagenomics referenced the idea that a collection of genes sequenced from the environment could be analyzed in a approach analogous to the study of a single genome. Metagenomicnext generation sequencing is simply consecutively all nucleic acids in a sample which may contain diverse populations of microorganisms and assigning these to their reference genomes to understand which microbes are present and at which proportions.
The identify nucleic acids and capability to sequence from multiple different class for metagenomic analysis which makes this a important platform that can be found to identify genetic material from entirely different class of organisms. Metatranscriptomics is the study of the function and activity of the complete set of transcripts i.e RNA sequencing from environment samples.
Metatranscriptomic sequencing provides straight access to culturable and non-culturable microbial transcriptome information by large-scale, high-throughput sequencing of transcripts from all microbial communities in specific environmental samples. Metatranscriptomic sequencing assign with opportunity to randomly sequence mRNAs as a unit to understanding the regulation of difficult processes in microbial groups.
The metatranscriptome be responsible for a picture of the gene expression in a given sample at a given moment and under specific conditions by capturing the total mRNA.
What Are the Metagenomics Next Generation Sequencing?
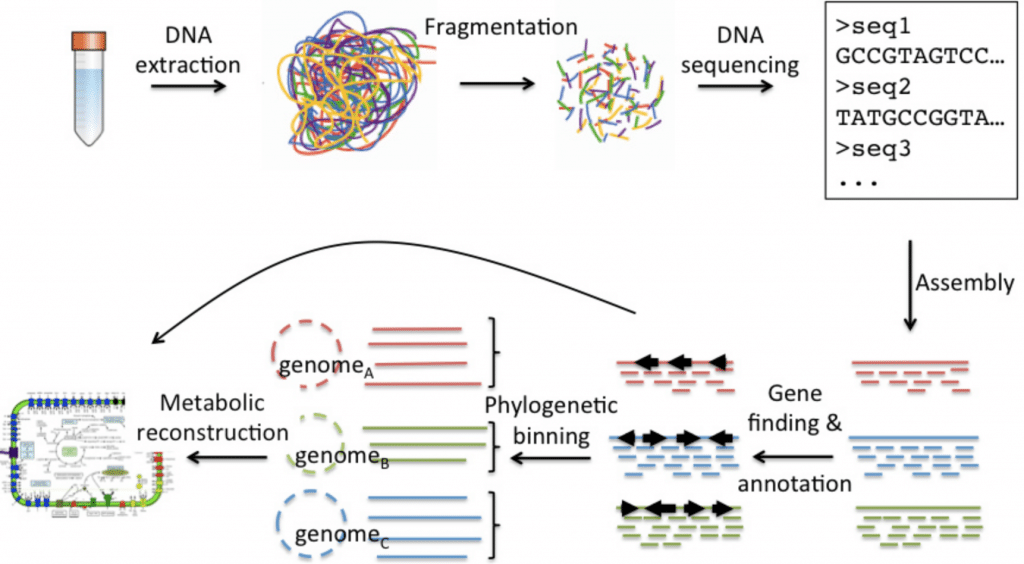
Sequencing is the process to find out the arrangement of all the deoxyribonucleotides in a genome, which help us to understand the potential alternation in some diseases. Because of the decrease in the cost, the importance of genome sequencing is prominent.
Because of cost and timing and length requirement of Sanger Sequencing, the sequencing technology did not contribute much in clinical and biological studies, until next generation sequencing technologies are invented. NGS technology is based upon the usage of dyed ddNTPs in Sanger methods.
The improvement is that NGS allows DNA strands to be amplified, detect and merge at same time leading to increase in length and efficiency of sequencing. NGS largely improves the efficiency and allow higher throughput detection that is why NGS is also called high-throughput sequencing and it is widely used in next generation sequencing technique.
To describe a bacterial genome using NGS the genome is split into multiple fragments that produces sequence or reads that are ranging from hundreds to ten thousands of bases in length. The sequences are arranged into a single genome using computational tools and techniques. Some of the overlapping sequence reads are assamble to produce a single longer sequence called a contig.
There are often gaps between contigs and though high accuracy longer sequence reads would be the perfect method of sequencing stages that produce shorter reads are generally less costly and the overlap in sequences are more accurate. The assembled genome which containing gap is aligned to a reference genome database for identification of the organisms.
This process represents a significant over the early days of sequencing when a single bacterial genome project might take several years.
The probable clinical applications are diagnosis of infectious diseases, outbreak tracking, mutation, infection control surveillance, and pathogen discovery and many more things. Metagenome next generation sequencing types are shotgun sequencing where clinical samples has been applied for different approaches like including , blood, gastrointestinal fluid, respiratory samples, cerebrospinal-fluid, and ocular fluid.
Why Metatranscriptome Analysis?
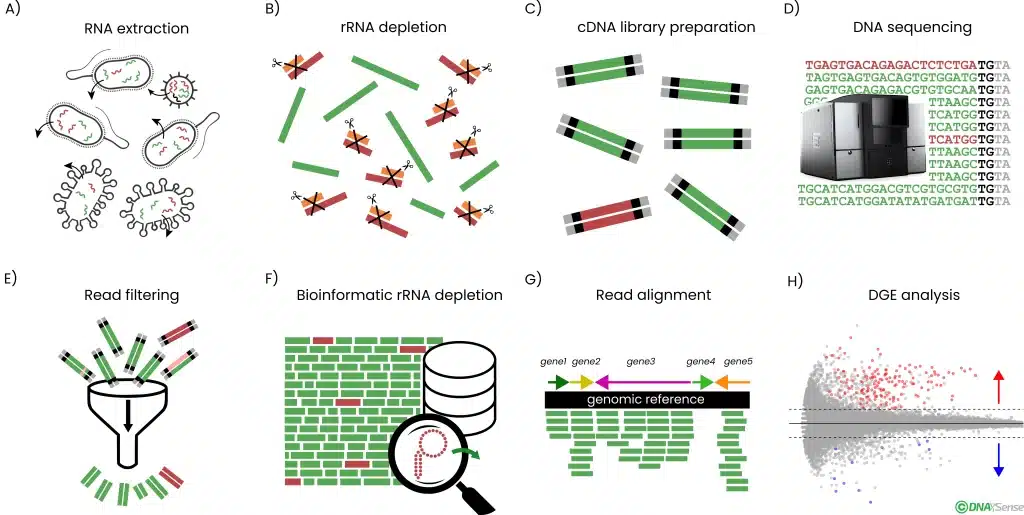
The study of the metatranscriptome through Next-Generation Sequencing techniques allows us to obtain gene expression profiles from whole microscopically populations, providing new insights into poorly known biological systems and overcoming technical limitations related to individual bacteria isolation.
Workflow for metagenomic next-generation sequencing
- Genomic DNA is extracted and fragmented
- Adaptors are attached for preparation of library sequencing and barcoding process.
- The fragments of DNA are sequenced together and independently
- Human related DNA sequence reads are removed
- from shorter and overlapping sequences Contigs of long DNA stretches are assembled.
Workflow of Metatranscriptomic Sequencing
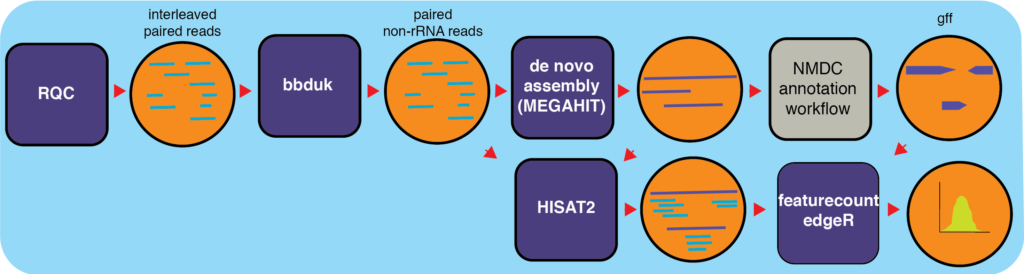
First step is to extract total RNA from the sample and after went for detection. The qualified RNA is subjected to database construction, fragment screening, and quality testing. The qualified library will be sequenced mostly using Illumina sequencing platform. The raw data acquired by sequencing will be used for bioinformatics analysis.
- RNA purification
- Library preparation
- RNA sequencing
- Filtering reads
- Annotation
- Statistical analysis
Process steps involved in Metagenome Sequencing
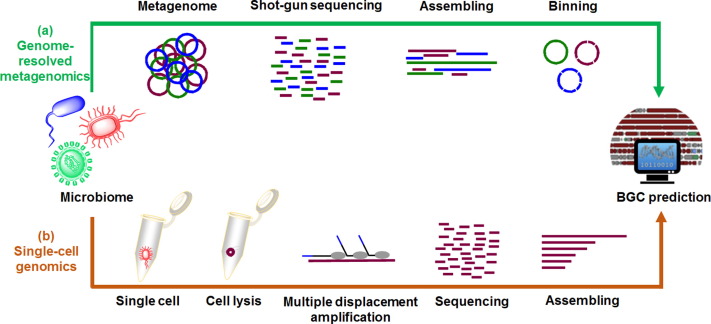
- Sampling
- Sample fractionation
- DNA extraction
- DNA sequencing
- Assembly
- Annotation
- Statistical analysis
- Data storage
- Data sharing
Sampling
Sample processing is the most important step in metagenomics. DNA extracted should be typical of all cells present in the sample and sufficient amount of high quality nucleic acid must be obtained for successive sequencing and library production.
Annotation
It is the process for identification of the genes, their regulatory sequences and their functions. Annotation also identifies non-protein coding genes, including those that codes for ribosomal RNA, transfer RNA and small nuclear RNAs. In addition, mobile genetic elements and repetitive sequence families present in the genome are also identified and characterized.
Statistical analysis
Metagenomic analysis involves the application of bioinformatics tools to study the genetic material from environmental, uncultured microorganism.
Bioinformatics tools used for analysis and interpretation
| Function | Software Tools |
| Detection of gene from genome sequencePrediction of a new gene | GENE SCAN, GLIMMER, GENIE, GRAIL, GENEMA RK, GENE FINDER, HMM GENE etc. |
| Identification of functional domain/motif of proteins | tBLAST, FASTA, HMMER |
| PRINTS, PROSITES,SMART, BLOCKS ETC | |
| Detection Of tRNA | tRNA scanase |
| Genome annotation· Description of experimental evidence· Indexing and visualization· Storage, manipulation, and visualization. | GAME, DAS Bio java 2001, Bio pearl 2001 etc. |
Steps involved in Metatranscriptome Analysis process
- Filtering reads – quality check-up of rRNA
- DOWNLOADED LIBRARIES
- De-multiplex
- Remove sequencing adapters
- Sequences trimming by quality
- Remove RNA
- ALIGNMNT/ASSAMBLY
- Aligning reads to a references – Map with bowtie2 or BWA
- De-novo assembly – assemble with velvet, SOAP de-novo or trinity cluster results
- ANNOTATION
- Annotate with BLAST, KASS OR M5NR
- STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
- Build and transform the matrix
- Establish sample similarity – Heatmaps, PCA, rlog etc.
- Analyse differential expression – heatmap and volcano graphs.
- Determine P value
- Give meaning to the data
Application of Metagenomics Sequencing?
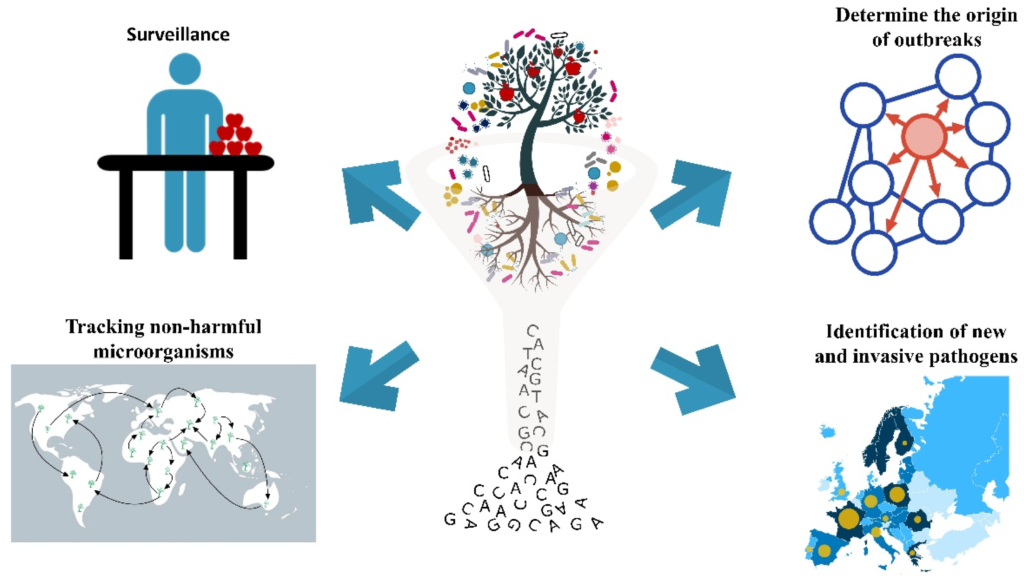
- Impartial results free from impact of specific genomic loci
- Independence from taxonomically informative genetic markers
- Have Ability to study extremely diverged microbes such as viruses.
- Close estimations of microbial diversity
- Detection of abundance of microorganisms in various environments
- Analysis of uncultured microorganisms
- Information on arrangement as well as functional abilities of an ecosystem
- function genes and gene clusters Investigation
Advantages of Metatrancriptomics
- A culture free method to expose the true level of microbial diversity
- Permitting function based activity screen
- Most targeted than shotgun random sequencing
- Cost efficient and time effectiveness
Benefits of Metagenomics and Metatranscriptomics Analysis using NGS
- Cost effectiveness
- Fast
- Ultra throughput (through screening )
- Cloning free
- Shorts read
Conclusion
While mNGS testing may likely play a major role in the microbiological diagnostic depends upon workflow in the future aspect particularly as sequencing and bioinformatic processing command progresses involved, this remains a high throughput technology for which the clinical effectiveness in our current medical practice environment remains undefined.
Although mNGS testing may offer novel and exciting diagnostic clinical opportunities in the future. current metatranscriptomic techniques are promising and there are still several obstacles that limit their large scale applications.
First, much of the collected RNA comes from ribosomal RNA, and its dominating abundance can dramatically reduce the coverage of mRNA, which is the main focus of transcriptomic studies.
To know more about the process workflow of Genomic Data Analysis using Next Generation Sequencing Data Analysis approach you can join us for a 3 Hour Short Course on Genome Analysis, register HERE
To know about the 4 key application of Next Generation Sequencing Data Analysis you can read it HERE
This article is originally published HERE







0 Comments